Lesson 13: What is Artificial Intelligence?
What is Artificial Intelligence (AI)?
This lesson introduces students to the concept of Artificial Intelligence (AI). It explains what AI is, how it works, and its real-world applications. By the end of the lesson, students will understand the different types of AI and how it is used in everyday life. The lesson will include explanations, examples, and interactive activities to help students grasp the key concepts.
Lesson Objectives:
- Define Artificial Intelligence (AI) and explain how it works.
- Understand the different types of AI (narrow AI, general AI, and super AI).
- Explore real-world examples of AI in various industries.
- Learn the ethical considerations and potential impact of AI on society.
Lesson Notes:
1. What is Artificial Intelligence (AI)?
Definition:
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is the simulation of human intelligence by machines. It involves creating systems that can perform tasks that normally require human intelligence, such as learning, reasoning, problem-solving, and decision-making.
Explanation:
AI allows machines and computers to “think” and “learn” from data in a way that mimics human intelligence. AI systems can make decisions, recognize patterns, understand language, and even perform tasks like driving cars or playing chess.
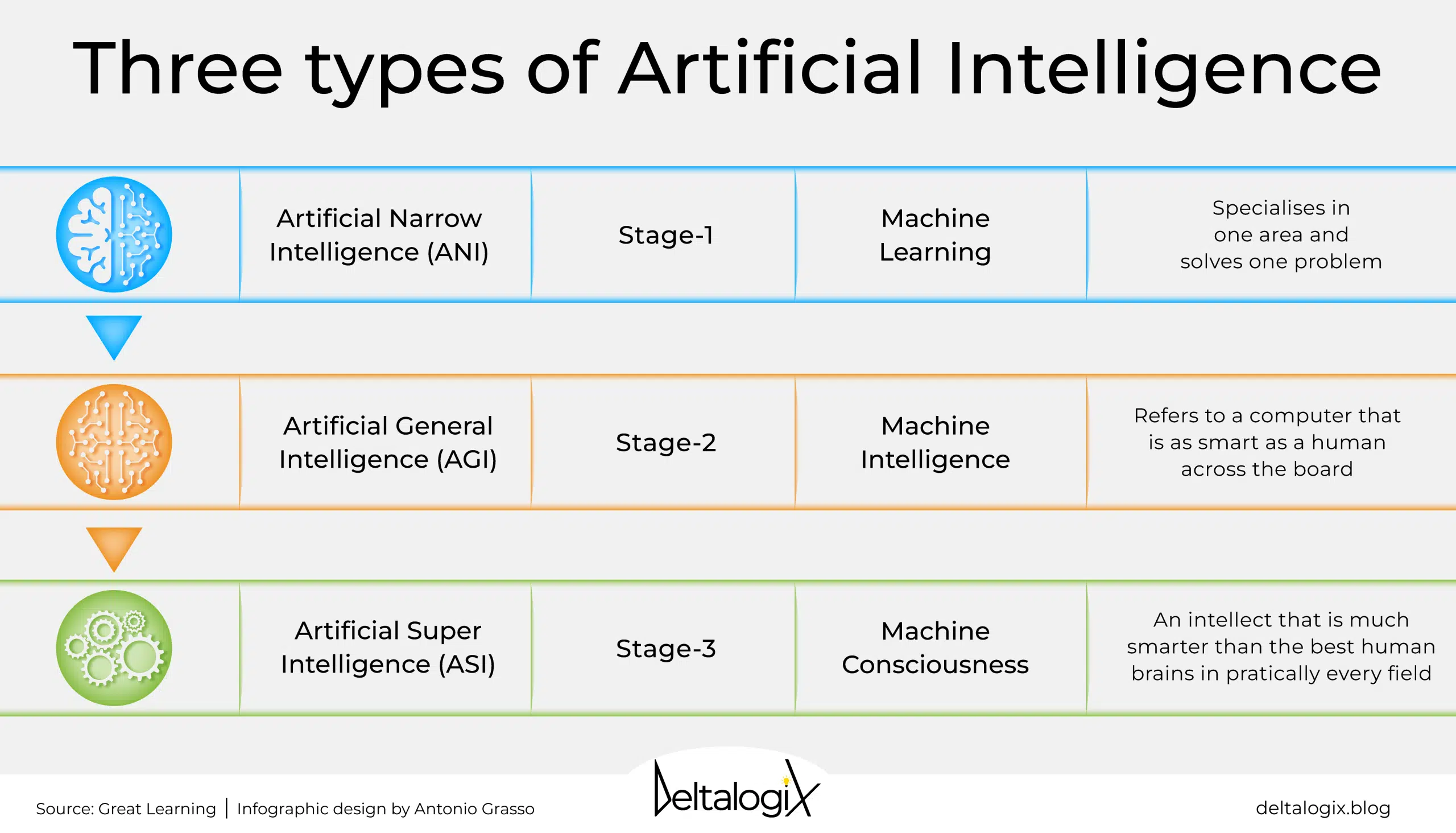
2. Types of AI
There are three main types of AI:
- Narrow AI (Weak AI):
Narrow AI is designed to perform a specific task or set of tasks. It’s the most common type of AI used today.- Example: Siri on iPhones is an example of Narrow AI. It can answer questions, set reminders, and send messages, but it cannot do anything outside its programmed functions.
- General AI (Strong AI):
General AI refers to machines that can understand, learn, and apply intelligence across a wide range of tasks, just like a human. However, this level of AI has not yet been achieved.- Example: General AI would be like a robot that can do anything a human can do, from cooking dinner to writing poetry.
- Super AI:
Super AI is a level of intelligence that surpasses human intelligence in all areas, including creativity, problem-solving, and even emotions. Super AI does not exist yet, but it’s the subject of many discussions about the future of AI.- Example: Super AI might be able to solve global issues like climate change or develop new technologies that humans can’t even imagine.
3. How Does AI Work?
AI systems are built using algorithms and machine learning techniques that allow them to learn from data. Here’s how it works in simple terms:
- Data Collection: AI systems are fed large amounts of data. This could be anything from images to text, videos, or numerical data.
- Training: The AI system uses machine learning algorithms to learn from the data. For example, it might learn to recognize images of cats by analyzing thousands of pictures of cats.
- Decision Making: Once trained, the AI can make decisions or predictions based on new data. For instance, after learning to recognize cats, the AI can now correctly identify a cat in a new photo.
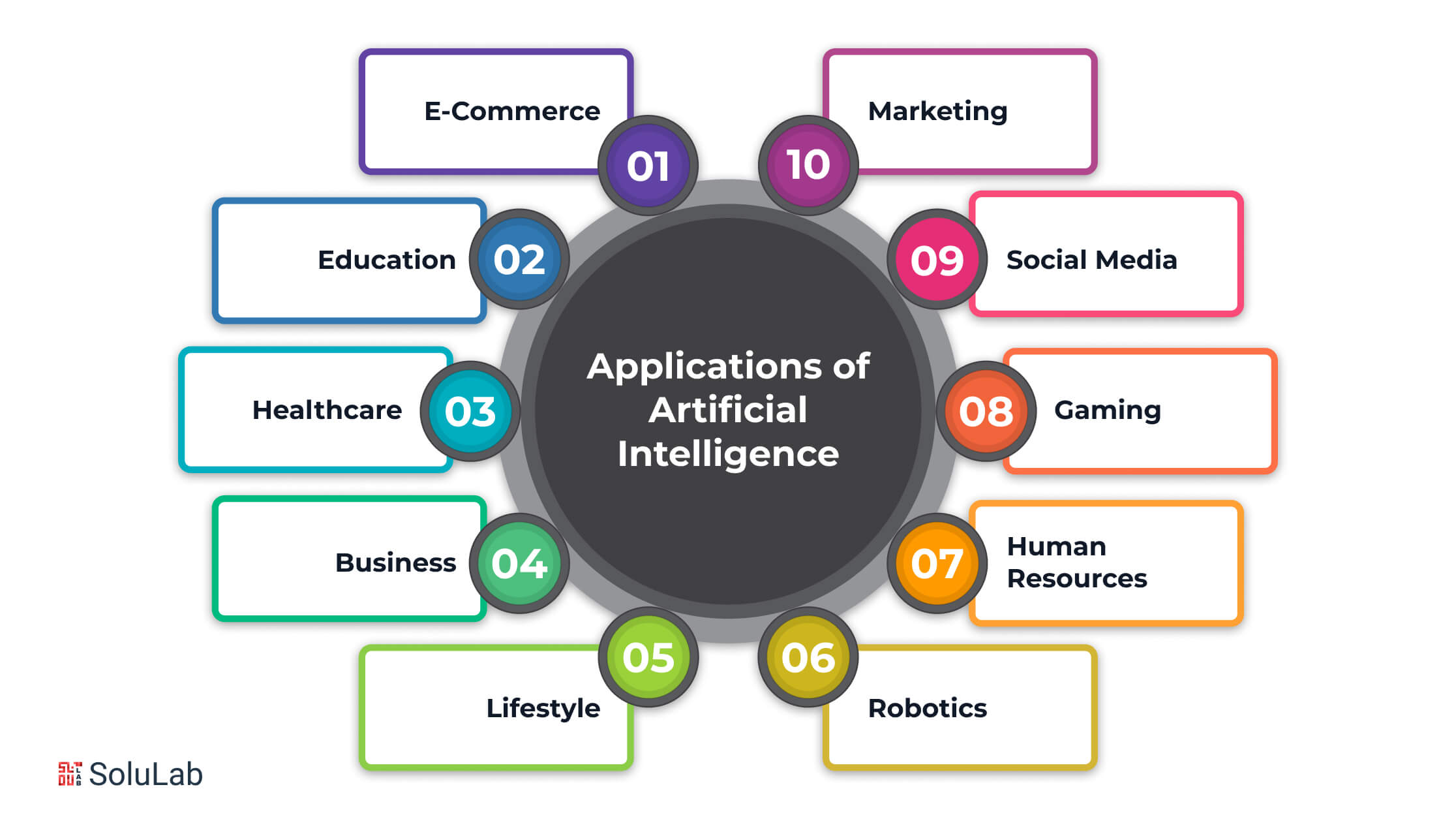
4. Real-World Examples of AI
- Healthcare:
AI is used in healthcare to diagnose diseases, analyze medical data, and even assist in surgeries.- Example: IBM’s Watson can analyze medical records and help doctors diagnose illnesses like cancer more accurately.
- Transportation:
AI is driving the development of self-driving cars.- Example: Tesla uses AI to enable its cars to drive autonomously, recognizing road signs, pedestrians, and other vehicles.
- Entertainment:
AI is used to recommend music, movies, and TV shows.- Example: Netflix uses AI algorithms to suggest shows based on your viewing history.
- Finance:
AI helps banks detect fraudulent transactions and manage investments.- Example: AI-powered systems can monitor transactions in real-time and flag any suspicious activity, protecting customers from fraud.
- Customer Service:
AI chatbots are increasingly being used to handle customer service inquiries.- Example: Companies like Amazon use AI-powered chatbots to answer customer questions, process returns, or track deliveries.
5. Ethical Considerations in AI
While AI offers many benefits, there are also ethical questions to consider:
- Job Automation:
Many jobs, especially in industries like manufacturing or customer service, are at risk of being replaced by AI. This raises concerns about unemployment and job displacement. - Bias and Fairness:
AI systems learn from data, and if the data is biased, the AI will also be biased. For example, facial recognition systems have been shown to have biases based on race and gender. - Privacy:
AI systems can collect and analyze huge amounts of personal data, raising questions about privacy and how this data is used.
Interactive Activity:
AI in Daily Life Exercise:
Have students make a list of the AI-powered devices or services they use daily (e.g., smartphones, Google Assistant, YouTube recommendations). Ask them to explain how AI helps improve their experience.
Real-World Application:
- :
Self-driving cars use AI to analyze road conditions, detect obstacles, and make decisions in real-time to safely navigate the roads. Companies like Tesla and Google are using AI to develop cars that can drive themselves, reducing accidents caused by human error.
- AI in Healthcare:
AI systems are being used to analyze medical images, such as X-rays and MRIs, to detect diseases faster and more accurately than doctors. For example, AI can help doctors detect early signs of cancer that might be missed by the human eye.
